DRUGS , SOPS,DETERGENTS,NARCOTICS AND ANTI-SEPTIC ALL DETAIL -
Drug :
A chemical substance which is used for the purpose of diagnosis, prevention, cure or relief of disease is called drug or medicine.
Ideal drug :
Ideal drug is one which
i) destroys hamrfull organisms but not harmless organisms
ii) does not disturb physiological processes.
iii) has minimum side effects
iv) should attack on affected site
v) it should not be habit forming
Chemotherapy :
It is a technique by which diseases are cured by suitable chemical compounds(i.e. drugs) .Classification of drugs :
Drugs are classified by different ways :I) Classification based on pharmacological effects of the drug :
These drugs affect normal processes of the body like digestion, blood circulation, breathing etc. e.g. Analgesic used as pain killer. ' Antibiotic and antiseptics stop the growth or kill the bacteria
II) Classification based on action of drugs :
These drugs are disease oriented. They have different mode of action. e. g. pain killer, antiarthritis, local anaesthetic agents etc.
III) Classification based on chemical structure :
Drugs are classified into different categaries like alcohols, ketones, hydrocarbons, esters, amides etc. Drugs having simillar chemical structure are expected to have simillar chemical properties. e.g. all sulphomides having simillar type chemical structure show antibacterial activity.
VI) Classification based on molecular target :
i) The drugs which interact‘target biomolecules are called target oriented drugs.
ii) The biomolecules like carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids etc, are target molecules with which drug interact
iii) This classificationis very important
V) Classification of drugs by lay public :
This classification depends upon the action of the drugs like analgesics, cough syrup, laxatives and purgatives,ointments, injections etc. |
Chemicals in medicines :
Depending on purpose for which they are used, medicines are classified as -
ANALGESICS
The drugs which relieve the pain by acting on central nervous system without loss of consciousness or wrthout much disturbing the nervous systemarecalled analgesises.
There are two types of analgesics
1)Norcotic 2) Non-norcotic
I) Narcotic analgesics :
They Produces sleep and unconsciousness. They are derivatives of opium. e.g. morphine, codeine, heroin
These drugs are habit fonning i.e. person gets addicted. They have some adverse effects.
2) Non-norcotic analgesics :
These drugs when consumed do not produce any significant depression of CNS. These are antiinflammatory and antipyretic. They do not form addiction e.g aspirin.
Aspirin:
It is common analgesic. It 15 acetyl derivative ofsaiicylic acid or 2-acetoxy benzoic acid. It IS obtained by acetylation of salicylic acid .Medicinal properties of aspirin :
i) Common analgesicii) Antipyretic
iii)Anti-inflammatory drug
iv) Antiblood clotting agent
v) Antirheumatic drug
Side effects of aspirin:
i) Toxic to liver
ii) Gastric irritant
iii) When taken in empty stomach, aspirin gets hydrolysed to salicylic acid which causes bleeding in stomach.
other non-norcotic drugs are paracetamol, ibuprofen, diclophenac sodium, diclophenac potassium.
ANTIPYRETICS
The chemical substances with reduces body fever are called antipyretics

aspirin, phenacetin,
analgin, novalgin etc.
TRANQUILIZERS
The chemical substances used to relieve or reduce the stress and anxiety leading to calmness are called tranquilizers .
These are used to relieve stress, mental tension mania (disorder of mood), insomnia (sleeping sickness), feeling of discomfort etc.
The mild tranquilizers used are equanil, valium, chlordiazepoxide, veronal, meprobarnate, serotonin.
Derivatives of barbituric acids called barbiturates are also used to control hypertension and depression. Barbiturates are hypnotic drug and produce sleep.
valium
merporbanmate
Side effects:
Headache, weight gain, discomfort ,blurring of Vision .
Working of tranquilizers in body:
Noradrenaline isone of the nemoti‘ansrrutters that play role 1n mood changes. If the level of noradrenaline is low for some reason, the signals sending become low and person suffers from depression In such situation antidepressant drugs are required which balance the level of noradrenaline
Iproniazid and phenefzine are used as mood elevators.
ANTIMICROBIALS
The drugs used to kill or stop the growth of micro organisms like fungi, bacteria, viruses are called antimicrobial .
The atimicrobial drugs are antibiotics, antiseptics and disinfectants.
1) Antibiotics:
Antiboitics are derived from micro-organisms and used to kill or prevent the growth of other microorganisms.
e.g. penicillin, streptomycin
a) Broad spectrum antibiotics :
These antibiotics are effective against all hannfull micro-organisms.
e.g. chlorompheniool, tetracycline, cephalosporin, chloromycetin, aminoglycosiders.
.
b) Narrow spectrum antibiotics :
These antibiotic kill or prevent the growth of specific microorganisms e. g. penicillin, Penicillin was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1 929
types of antibiotics :
i) Bactericidal : They kill the micro-organism
ii) Bacteriostatic : They strop the growth of micro-organism.
Bactericidal Bacteriostatic
l) Penicillin i) Erythromycin
ii) orlaxaein ii) Tetracycline
iii)Amino glycosiders iii) Chloramphenicol .
iv) Cephalosporin
Streptomycin is bacteriostatic in low concentration and bactericidal in high concentration.

ampicillin and anoxycillin are semisynthentic modifications of penicillin . these are broad spectrum .
2) Antiseptics:
The drugs which are applied to the living tissues to kill the bacteria and to stop their growth in wound,thus preventing Its infection are called antiseptics. They are used in talcum powder, deodorants, soaps,breath purifiers, shampoos.
e ..g
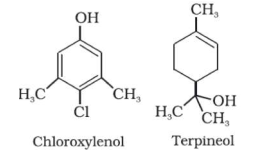
i) Dettol , it is a mixture of terpeneol and chloroxylenol.

ii) Tincture of iodine 2-3% solution of iodine in ethyl alcohol and water. It is powerfull antiseptic.
iv) H3BO3 (boric acid) is mild antiseptic used for eyes.
v) dil. Phenol
vi) H2o2 under the name perhydrol
vii) CHI3.(lodoform)
3) Disinfectants :
The chemical substances that are applied to non-living objects to kill the micro-organisms are called disinfectants. .
They are used in public health sanitation, floors, steralise instruments.
e.g. Cl2 , SO2 phenol
Dil. solution of phenol is used as an antiseptic where as concentrated phenol is used as disinfectant.
ANTIFERTILITYDRUGS
Antifertility drugs are used to control population:
The chemical substances which control the pregnancy are called antifertility drugs. These drugs are a mixture of synthetic estrogen and progesterone hormones.
e. g. Novestrol (estrogen derivative) Norethindrone (progesterone derivative)
ANTACIDS
The Chemical substances which neutrallses the excess of acid.in stomach and raise the pH of stomach to appropriate level are called antacids.
Acidity is due to the secretion of HCl in gastric Juices.
The commonly used antacids are
ii)Baking soda (NaHCO3).
ii) MgO, Mg(OH)2, MgCO3 and magnesium trisilicate . '
iii) CaCO3 _
iv)Al(OH)3,AlPO4
Omeprazole and lanSOprazole prevent the formation of acid in stomach. Ranitidine (zantac) and cirnitidine (Tegamet) are also used as antacids. Some other examples are digene,gelusil, aciguard etc.
Ranitidine(Zantac)
ANTIHISTAMINES (ANTIALLERGIC DRUGS)
The drugs which inhibit or reduce the action ofhistamine 1n the body there by preventing allergy are called antihistamines. '
Number of different sensitising substances (called antigens) derived from food or environment may cause allergic reaction in human. This is due to release of chemical substance called histamine inthe body.
Histamine in stomach stimulate the secretion of HCl and pepsin. Antihistamines compete with histamines for the binding sites of receptors and prevent allergy.
CHEMICALS IN FOOD
the process of fermentation, acidification or other decomposition of food by growth of microbes are called presevatives.
Food preservatives retain colour, texture, flavour, nutritive value of food. The latest methods used for food preservation are vacuum packing, freeze drying, U.V. or ionizing radiation to control micro-organism growth, irradiation by y-rays.
I) Physical methods for preservation of food :
i) By removal of heat (By cooling) :i It involves refrigeration, freezing preservation, dehydrofreezing preservation or carbonation. Due to cooling, growth of micro-organism is lowered. Fish, meat, vegetables, fruits are stored by this method.
2) By addition of heat :
Strong heating kill the micro-organism :
It includes stationary and agitating pastereurisation or sterilization.
Solid and liquid foods are preserved by this method.
e. g. milk is pasteurised for preservation.
3) By removal of water (Dehydration) :
Water is removed by sun drying, low temperature evaporation, freeze drying or puff drying. As gamer is removed, the growth of micro-organism is prohibited. Food graims, fruits, vegetables are preserved by this method.
4) By irradiation :
UV or ionizing radiations or y-rays or electron beam are used to preserve food. The irradiation kill the micro-organisms.
Milk and fruits are preserved by this method, sprouting of potatoes and onion is prevented by y-rays.
II) Chemical methods:
1) Addition of sugar :Here food is heated with sugar to the point of crystallisation and then dried. High concentration of sugar remove water by osmosis and growth of micro-organism is retarded. This is cheap and easy method. . Fruit j ams,jellies are preserved by this method.
2) Addition of salt :
Salt has water retaintion property. It remove the water causing dryness and death of microbes.pickles, fishes are preserved by salting, lemon, chillies, raw mango are preserved by this method.
3) Addition of vinegar :
Vinegar is 6 to 10% acetic acid. It preserve pickles, salad dressings, mustard, fish etc.
4) Addition of chemicals :
Chemicals like sodium benzoate, salts like sorbic acid and propionic acid are used as preservatives.
Artificial Sweetning Agents :
The chemical susstances which do not occur in nature but are synthesised in laboratory, have sweet
taste, no food value are called artificial sweetning agents or artificial sweeteners. They do not increase any calorie, are non digestable. It is excreted as such in urine.
e.g.
Saccharin,
Sodium salt of saccharin
Saccharin is 550 times more sweet than sucrose. Saccharin is insoluble in water but its sodium salt is soluble in water.
Some other artificial sweeteners
Sucaralos : It is trichloro derivative of sucrose. It is 600 times sweeter than sucrose,. It is unstable at high temperature hence not used in cooking.Alitame :It is 2000 times sweeter than sucrose and stable at high temperature.
Aspartame : It is about 100 times sweeter than sucrose. It is unstable at higher temperature. Hence only used in cold foods.
Artificial sweeteners are used in
i) Soft drinks, cold drinks,
ii) Baked goods,
iii) Medicines,
iv) Toothe paste
v) Chewing gums,
vi) Canned foods
ANTIOXIDANTS
The substances which when added to food, retards or prevents oxidative deterioration of food are called antioxidants.
Antioxidant prevent the rancidity of oils and fats. During oxidation of food, free radicals are generated. The antioxidants react with these free radicals and stops further oxidation of food.
1)BHT : Butylated hydroxy toluene

2,6-di(2-methyl-2-propyl) 4-methy1 phenol
Fat react with oxygen to from free radical, which react further with BHT to form stable BHT free radical. This freé radical does not react with fat, thus stop the chain reaction. This prevent rancidity of fats
2) BHA: Butylated hydroxy anisole:
2-(2-methy1-2-propyl) 4-methoxy phenol
It is used to preserve fats from becoming rancid. It is used in cosmetics, pharmaceutical, animal feed and in butter, chewing gum, baked food, beer and dehydrated potatoes.
3) SO2 and Sulphites :
S02, sodium metabisulphite (Na2S205) potassmm metabisulphite (K2S2O5) are used to prevent growth 1 of microbials.
SO2 act as preservative and also antioxidant for dried fruits, vegetables, soft drinks and alcoholic beverages.
Sulphite are used as antioxidants and reduce discolouration of fruits, vegetables, preservative for wine, dairy products, sauce, jams, jellies etc.
CLEANSING AGENTS
Soaps and detergents are used as cleansing agents.
Soaps : Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of higher fatty acids containing more than 4,2 an atoms
Soaps are represented by R-COONa or R-COOK. Potassium soaps are soft soaps and are used in shampoo, shaving cream and bathing soaps. Sodium soaps are hard soaps and are used in toilet soap and used for washing purpose.
Preparation of soaps :
Soaps are prepared by two ways1) By hydrolysis of fats (Triglycerides):
When oil or fat is hydrolysed by dil. NaOH or KOH, soap is obtained . This reaction is called
saponitication.
Formed soap and glycerol are separated by adding salt Soap is insoluble 1n salt solution, precipitates out due to common ion effect and glycerol remain in a solution as it is soluble.
2) By neutralization of fatty acids :
When fatty acids are neutralised by dil. NaOH or NazCO3, soaps are obtained.R-COOH + dil .NaOH ------ (R-COO- )(Na+) + H20
higher fatty acid soap
Soaps are not used in hard water:
Soaps are insoluble in hard water. Hard water contain metal 1ons like Ca2 and Mg2+ . These ions react with soap and form white curdy ppt. of calcium and magnesium salt.
soap insoluble salt
This ppt stick to the cloth and blocks cleansing action of soap. This wastes the soap.
Detergents :
Synthetic detergents are formulated products containing either sodium salts of alkyl hydrogen sulphate or sodium salts of long chain alkyl benzene sulphonic acids.
Detergents are superior to soaps. Detergents can be used in soft and also in hard water.
Types of detergents :
There are three types :l) Anionic detergents :
These detergents are sodium salts of sulphonated long chain alcohols or hydrocarbons.
Long chain alcohols or hydrocarbons are reacted with concentrated H2S04 to form alkyl hydrogen sulphate, which is neutralised with alkali to form salt.
2) Cationic detergents:
Cationic detergents are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with acetate, chloride or bromide
n-hexadw tnmethyl amm. chloride (or cetyl tnmethyl amm. chloride)
In cationic detergents , the cationic part (+ve part) of molecule is hydrophilic and involved in cleasing action.
They have germicidal property and used in hair conditioners.
3) Non-ionic detergents:
They non-ionic like esters of high molecular mass. They contain polar group which can form hydrogen bond with water.These detergents are either monoesters of polyhydnc alcohols or polyethers derived from ethylene
oxide
Mechanism of cleansing action of soap and detergent:
Soap and detergents have two parts. A long chain of hydrocarbon (tail) soluble in oil and other part (head) soluble in water. It form emulsified oil droplets in watér and are removed from cloth .The anions of emulsion repel to each other and cannot reprecipitate.
Detergents are superior to soaps :
i) Detergents are soluble in hard water but soaps are insoluble in hard water, hence soaps are not used as cleansing agent in haed water .
ii) Synthetic detergents can be used in acidic solution while soaps precipitates in acidic solution.
iii) Synthetic detergents are easily soluble in water and produce more leather than soaps. Hence detergents are superior to Soaps.
How are detergents and soaps used check hardness of water?
ii) Soaps get precipitated to from insoluble salts of calcium and magnesium in hard water but detergents do not form any precipitate.
iii) Hence soaps are used to check hardness of water.
How detergents cause water pollution?
i) Detergénts contain 20% active ingredients and remaining are sodium sulphate, inorganic phosphates, perborgy foaming agents.
ii) phosphates from detergents assists algae and weeds to grow in water, which deplete the oxygen for sea animals .
iii) Hence detergents cause water pollution.
‘


















No comments:
Post a Comment