CONDENSER
A closed vessel in which stream is condenser by absorbing the heat and where the pressure is maintained below the atmospheric pressure is known as condenser .
YOU TUBE VIDEO LINK - CLICK FOR VIDEO
YOU TUBE VIDEO LINK - CLICK FOR VIDEO
ELEMENTS OF STEAM CONDENSER PLANT -
1 . CONDENSER -
It is a closed vessel heat exchanger in which the steam coming from turbine is condensed using a supply of cooling water at atmospheric temperature . the quality of cooling water required to condense the steam in the condenser is considerably about 16 to 100 kg / Kg of steam
2. CONDENSER COOLING WATER-PUMP AND MAKE UP WATER PUMP -
Circulation of water through the condenser is maintained by the Cooling water pump . some cooling water is lost ( 1 to 2% of total) therefore this water is supplied by separate pump knowing eyes makeup water pump .
3. CONDENSATE EXTRACTION PUMP -
The condensate cannot flow from low pressure in the condenser to the atmospheric pressure the function of condensate pump is to extract the condensate from the condenser where the pressure is below atmospheric and feed it to the hot well where the pressure is atmospheric .
4. hotwell -
the hot well is sump between the condenser and the boiler where the condensate coming from the condenser is collected
5 . Boiler feed pump -
Boiler feed pump is used to pump the condensate from or 12 into the boiler by increasing the pressure of the condenser above boiler pressure
6 . air extraction pump -
the function of air extraction pump is to extract the air which has Into the condenser by various part . to maintain the required Vacuum inside .
7 . cooling tower -
in many plants large amount of cooling water required is not available Throughout the year in the river . under search circumstances the hot water coming out of the condenser Is cooled up by forcing it through out the cooling tower instead of discharging it to the downward site of river the cold water is reversed in the condenser . the loss of water by vaporization and leakage is compensate by make-up water pump taking the water from the river or some other sources .
classification of condenser
1. Jet condenser / mixing condenser
2. surface condenser
Jet condenser -
there is a direct contact between steam and cooling water and heat exchange is by direct condensation it is classified as :
- High level Jet condenser / barometric condenser
- Low level Jet condenser/ parallel flow Jet condenser
- counter flow Jet condenser
- Ejector condenser
High level Jet condenser -
it is also called as barometric Jet condenser because the sale is placed at the height greater than the barometric height of the water column ( 10.363 m) . In barometric condenser that tailpipe is more than 10.363 m m in height is used and thus making it impossible for any vacuum in the condenser to cause water to rise high in the tail pipe .
The height of Shell much above the barometric hai necessitate a separate pump for injecting cooling water from cooling pond . there is no need of water extraction pump . the condensate and cooling water flow out of the condenser by GravityTo the hot well and maintain the column of water in water lag , which will depend upon the vacuum in the condenser . air released from condenser Esteem passes upward through the Falling cold water and get cooled . The removed by separate dry air pump .
low level / parallel flow -
Low level parallel flow Jet condenser occupied with a dry air pump and a condensate extraction pump . the mix of exhaust steam and air from the engine intas 2 top of the condenser and while travelling downward come in the contact with spray of cooling water . the cooling water enters from the top and its broken in finance Team by suitable arranged buffles . the condensate gets progressively cooled as it goes down and this increases the plant efficiency .
Counter flow condenser -
the cooling water enters of the top cascade downward through a series of perforated trays . the spend steam enters near the bottom . in the arrangement there is a no under cooling of condensate and the temperature of condensate main approaches as that of steam . to bring out condensation of steam loss amount of cooling water will be required . the vacuum created by air pump is safeCool water into the condenser here and there is a no need of cooling water pump .
surface condenser -
the heat is continuously transferred through a well interposed between steam and cooling water they are again classified As,
- Down flow condenser
- Central flow condenser
Down flow surface condenser -
she goes to pass down flow surface condenser the to pass arrangement is compact , more efficient in the process of heat exchange and is to be preferred when supply cooling water is less .
the section of extraction pump is installed at the bottom , causes the paint steam enter from the top of floor downward over the nest of tubes . the cooling water intas at the one end of bottom set of tubes flow through them till it reaches to the other end of shell . The water that rise up and flows in the opposite direction from the upper half of the tubes and finally live through the outlet . A section of pubes near the air pump suction is screen of providing a buffle . This is done to reduce the amount of water vapour going along with air . more over the lower temperature maintained in this section increases the density of air and so we need extraction pump of small capacity .
evaporative condenser -
the steam to be condensed enters a coiled find a pipe at one end . the water from cooling Pond is pumped horizontal header . which is fitted with spray nozzles . the cooling water spread over the tubes get separated by absorbing heat from the steam . the steam loserBoth to cooling water and the current of air circulating over Water tubes . the remainder of water cooling water fall into the cooling pond and loss of water evaporated is replenished by the adding of quality of cold makeup water . The header air moves upward carrying with it a portion of cooling water you have written into vapour . the arrangement is simple , cheap does not require large quantity of cooling water and soap needs cooling water pump of small capacity . the vacuum created is however not so high as the surface condenser .
Central flow type -
in this type of condenser the section pipe of the air extraction pump is located in the centre of the tubes which results in radial flow of the steam . the better contact between the outer surface of the tube and the steam evaporate , due to large passages the pressure drop of steam is reduced .
inverted flow type -
this type of condenser has the air suction at the top the steam after entering at the bottom Rises up and then again falls down to the bottom of the condenser by following a path near the outer surface of the condenser . . the condenser extraction pump is at the bottom .
regenerative type -
this type is applied to condenser adapting regenerative method of heating of the condensate after having the tube nest , the condensate is passed through the entering exhaust steam from the steam reparation or turbine the rising the temperature and the condensate for us as feed water from the boiler .
condenser efficiency -
there is a no standard method for specifying efficiency of condenser . a method suggested by person and co . well Of steam turbine has widely used
condenser efficiency = T wo - T wi
Ts - T wi
T wi = Temperature of cooling water at inlet.
T wo = temperature of cooling water at outlet.
Ts = temperature of steam corresponding to the actual absolute pressure in the condenser.
Vacuum efficiency = Pb - (Pa + Ps)
Pb - Ps
= Pb - Pt
Pb - Ps
Ps = Saturated pressure of steam in bar corresponding to the temperature of the water entering
in the condenser .
Pt = ( Pa + Ps ) - Total pressure of steam in condenser .
Pb = Atmospheric pressure or barometric pressure .
advantages of condenser -
improvement in the efficiency of plant due to increased available enthalpy drop .
- reduction in steam consumption per hour, increase in vacuum from 71 to 73.5 CM of HG. dudes above 45% reduction in steam consumption .
- the condensed steam called condensate is collected in hot well maybe pumped back to the boiler as feed water . recovery of condensate reduce the makeup water that should be added by system from hundred percent when non condensing to 1.5% when condensing from the steam power plant where sufficient quantity of good quality Boiler feed water is not available recovery of condensate is very important example Marine power plant .
- the prevent the corrosion and arising of the boiler due to fill water which is not available in pure form the recovery of condensate reduce the capital and running cost of water softening paint .
- provision for the supply of hot water to the boiler results in the fuel economy and safety from thermal stresses .
Cooling tower :
Cooling tower is an hour artificial device used to cool the hot cooling water coming out of the condenser more effectively. the principle of cooling water in cooling tower is similar to that of evaporative condenser some percentage of total water ( 1%) goes into ear in the form of water vapour taking it latent heat from the remaining water and call Action in the temperature of water .
cooling tower is an important unit in the condenser plant it is used for cooling off the condenser circulating water so that it can be recirculated through the condenser .
Classification
on the basis of material used :
- Timber
- Concrete
- Steel duct type
Timber type cooling tower :
Timber cooling tower is rarely used due to following disadvantages
- Tendency of timber to crack due to exposure of sun wind water etc .
- short life time and high maintenance cost .
- not proper circulation of air .
- Limited cooling capacity .
Concrete type cooling tower :
concrete cooling tower are becoming popular with modern power plant .
main advantage in this are :
- Low maintenance cost
- increase the stability
- large capacity sometime of the order of 5 x 10^ 5 Litre per hour
Steel deck type cooling water Tower
Steel deck type cooling tower are rarely used in modern power plants .
main advantage in this are
- Small capacity in order to increase the rate of exchange
- air is some time for slow through cooling tower by means of suitable fans
- in this case cooling of water Takes place so that they are independent of atmospheric conditions .
On the basis of draught
- Natural draft
- forced draft
Inducted draft cooling tower -
the arrangement of inducted draft cooling tower is showing figure . the hot water coming out from the condenser is separated at the top of Tower and air is conducted to flow through the tower with the help of inductor draught fan mounted at the top of the tower as shown in the figure . the water lost in cooling Tu average from 1 to 2% by evaporation and 0.5 to 2% by different process . to make up these laws makeup water is supplied .
the rate of evaporation and effect of cooling depends upon
- Amount of water surface exposed to air
- the time of exposure
- relative humidity of the air passing through the tower
- direction of the airflow relative to the water flow .
advantages of forced draft cooling tower :
1 . these are comparatively compact in size with low weight .
2 . the draught that is movement of air through the cooling tower is created by employing mechanical means like a fan of 10 at top of Tower.
3. the fan induced the flow of cool air from the ambient .
4 . in the cross flow arrangement air enters in rapidly in one direction and flow horizontally on word .
5 . water enters at top and Falls through a packing material . Breaking the water into small droplets to increase the exposed area of contact for improved heat transfer .
6 . a small evaporation loss of water occurs during heat transfer .
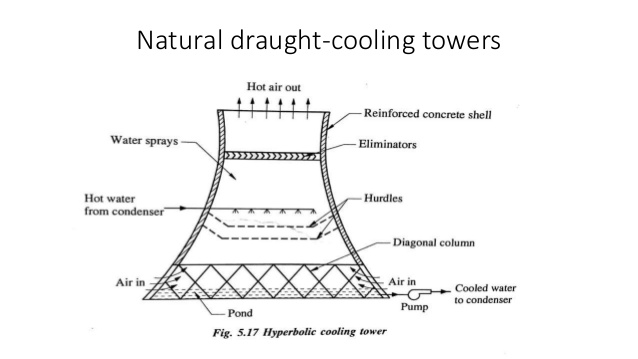
Natural draft cooling Towers :
large plants also use this type of cooling tower . these are very large in size compared to tower using fan to provide the same amount of cooling . pressure is created by natural air velocity .
- Natural draught with Tower employee a Chimney effect for moving the ambient air, the chimney effect is created by huge hydraulic power serving nozzle action .
- the hyperbolic Tower constructed for RCC work has a base diameter running between 75 to 200 metre and height between 100 to 150 m .
- in the cross flow arrangement water is spread the word near to the base of Tower and air is induced rapidly invert due to Chimney effect .
- in the counter flow arrangement air enters through a peripheral section through a descending water spray made from suitable height .
- natural draught with Tower are also effective in the are 4S having low reactive humidity of ambient air producting a comparatively strong buayanal effec .
comparison table -
forced draft tower
|
inducted draft Tower
|
|
|







No comments:
Post a Comment